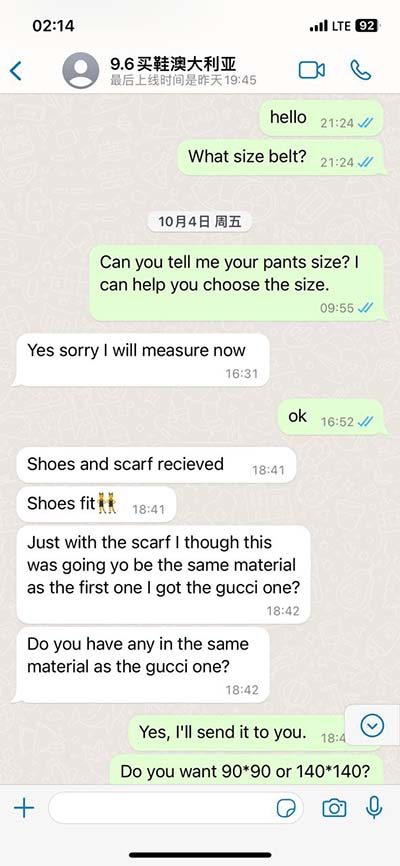
lv global longitudinal strain | time to peak longitudinal strain lv global longitudinal strain A, Baseline echocardiogram shows normal left ventricular strain (2-dimensional global longitudinal strain). B, Reduced global longitudinal strain with a . ACE English Malta is a Boutique and state-of-the-art school. We bring the latest education methodology and technology to our interactive, exclusive custom-made lessons.
0 · time to peak longitudinal strain
1 · reduced global longitudinal strain
2 · longitudinal strain maps from echocardiogram
3 · global longitudinal strain treatment
4 · global longitudinal strain prognosis
5 · global longitudinal strain chart
6 · Lv strain normal values
7 · Lv strain echo normal values
Relax on the front porch of the Old House at Peace field. Adams National Historical .
Learn how echocardiographic global longitudinal strain (GLS) can be used to monitor cancer chemotherapy-related cardiac dysfunction. Find out the definition, derivation, analysis, and interpretation of GLS, and common errors to avoid.
There is growing evidence that patients with severe aortic stenosis and LVEF 50-60% have . Left ventricular (LV) global longitudinal strain (GLS) is a measure of the active shortening of the LV in the longitudinal direction, which can be assessed with speckle-tracking . Global longitudinal strain (GLS) is prognostic of adverse cardiovascular outcomes in various patient populations, but the prognostic utility of GLS for long-term cardiovascular .
A, Baseline echocardiogram shows normal left ventricular strain (2-dimensional global longitudinal strain). B, Reduced global longitudinal strain with a . Speckle tracking echocardiographic global longitudinal strain (GLS) predicts outcome in patients with new onset heart failure. Still, its incremental value on top of left .Normal global circumferential strain varied from -20.9% to -27.8% (mean, -23.3%; 95% CI, -24.6% to -22.1%). Global radial strain ranged from 35.1% to 59.0% (mean, 47.3%; 95% CI, 43.6% to .Global longitudinal strain (GLS) has emerged as a fine-tuned, highly reproducible, and operator-friendly method for quantification of left ventricular function and prognostication in a wide .
There is growing evidence that patients with severe aortic stenosis and LVEF 50-60% have a higher rate of adverse outcomes compared to patients with LVEF >60%. A meta .This review article focuses on the practical aspects of measuring LV global longitudinal strain (GLS), reviews the clinical implications of impaired LV GLS strain and provides a glimpse into the future clinical applications of this .The reference ranges for left ventricular (LV) global longitudinal strain and right ventricular free-wall strain were −24% to −16% and −35% to −17%, respectively. Correspondingly, left atrial .
GLS is a simple parameter that expresses longitudinal shortening as a percentage (change in length as a proportion to baseline length). GLS is derived from speckle tracking, and analyzed by post-processing of apical images of the LV. Left ventricular (LV) global longitudinal strain (GLS) is a measure of the active shortening of the LV in the longitudinal direction, which can be assessed with speckle-tracking echocardiography. Global longitudinal strain (GLS) is prognostic of adverse cardiovascular outcomes in various patient populations, but the prognostic utility of GLS for long-term cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in the general population is unknown.A, Baseline echocardiogram shows normal left ventricular strain (2-dimensional global longitudinal strain). B, Reduced global longitudinal strain with a nonspecific pattern, consistent with trastuzumab-induced cardiomyopathy.
Speckle tracking echocardiographic global longitudinal strain (GLS) predicts outcome in patients with new onset heart failure. Still, its incremental value on top of left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) in patients with nonischemic, nonvalvular dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) after optimal heart failure treatment remains unknown.
Normal global circumferential strain varied from -20.9% to -27.8% (mean, -23.3%; 95% CI, -24.6% to -22.1%). Global radial strain ranged from 35.1% to 59.0% (mean, 47.3%; 95% CI, 43.6% to 51.0%). There was significant between-study heterogeneity and inconsistency.Global longitudinal strain (GLS) has emerged as a fine-tuned, highly reproducible, and operator-friendly method for quantification of left ventricular function and prognostication in a wide spectrum of cardiac diseases (3). There is growing evidence that patients with severe aortic stenosis and LVEF 50-60% have a higher rate of adverse outcomes compared to patients with LVEF >60%. A meta-analysis suggests that impaired LV GLS despite LVEF >50% is associated with reduced survival.
time to peak longitudinal strain
This review article focuses on the practical aspects of measuring LV global longitudinal strain (GLS), reviews the clinical implications of impaired LV GLS strain and provides a glimpse into the future clinical applications of this technology.The reference ranges for left ventricular (LV) global longitudinal strain and right ventricular free-wall strain were −24% to −16% and −35% to −17%, respectively. Correspondingly, left atrial (LA) and right atrial (RA) reservoir strains were 17% to 49% and 17% to 59%.
GLS is a simple parameter that expresses longitudinal shortening as a percentage (change in length as a proportion to baseline length). GLS is derived from speckle tracking, and analyzed by post-processing of apical images of the LV.
Left ventricular (LV) global longitudinal strain (GLS) is a measure of the active shortening of the LV in the longitudinal direction, which can be assessed with speckle-tracking echocardiography. Global longitudinal strain (GLS) is prognostic of adverse cardiovascular outcomes in various patient populations, but the prognostic utility of GLS for long-term cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in the general population is unknown.A, Baseline echocardiogram shows normal left ventricular strain (2-dimensional global longitudinal strain). B, Reduced global longitudinal strain with a nonspecific pattern, consistent with trastuzumab-induced cardiomyopathy.
Speckle tracking echocardiographic global longitudinal strain (GLS) predicts outcome in patients with new onset heart failure. Still, its incremental value on top of left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) in patients with nonischemic, nonvalvular dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) after optimal heart failure treatment remains unknown.Normal global circumferential strain varied from -20.9% to -27.8% (mean, -23.3%; 95% CI, -24.6% to -22.1%). Global radial strain ranged from 35.1% to 59.0% (mean, 47.3%; 95% CI, 43.6% to 51.0%). There was significant between-study heterogeneity and inconsistency.Global longitudinal strain (GLS) has emerged as a fine-tuned, highly reproducible, and operator-friendly method for quantification of left ventricular function and prognostication in a wide spectrum of cardiac diseases (3).
There is growing evidence that patients with severe aortic stenosis and LVEF 50-60% have a higher rate of adverse outcomes compared to patients with LVEF >60%. A meta-analysis suggests that impaired LV GLS despite LVEF >50% is associated with reduced survival.This review article focuses on the practical aspects of measuring LV global longitudinal strain (GLS), reviews the clinical implications of impaired LV GLS strain and provides a glimpse into the future clinical applications of this technology.
reduced global longitudinal strain
omega seamaster 007 casino royale

2017 omega seamaster 300

longitudinal strain maps from echocardiogram
Chanel has named Ugandan-Canadian actress Whitney Peak as its first Black fragrance ambassador. The 20-year-old is the new face of Coco Mademoiselle, .
lv global longitudinal strain|time to peak longitudinal strain